
Life and Sport Game Changer | Metabolic Efficiency
Life begins and ends at the cellular level.
The foremost nutrition limiter to endurance sports performance is depleted glycogen stores. Reliance by many athletes on carbohydrates [CHO] as their primary fuel source remains pervasive and indefensible because it sabotages one’s health and potential.
‘Two roads diverged in a wood and I – I took the one less traveled by, and that has made all the difference.’
~Robert Frost
_________
Enter Metabolic Efficiency [ME].

Endurance athletes erroneously fixate on replenishing the limited supply of CHO [1,200 calories] in the tank while transporting nearly unlimited fuel stored as endogenous fat [80,000 calories].
Bob Seebohar, a certified Specialist in Sports Dietetics, displaying a coaching resume’ of Olympians, professional athletes, and collegiate teams, bluntly lays it out: ‘The best training plan is worthless if the nutrition plan fails.’
Consuming protein, fiber, and healthy fat represents the nutritional foundation of Metabolic Efficiency [ME].
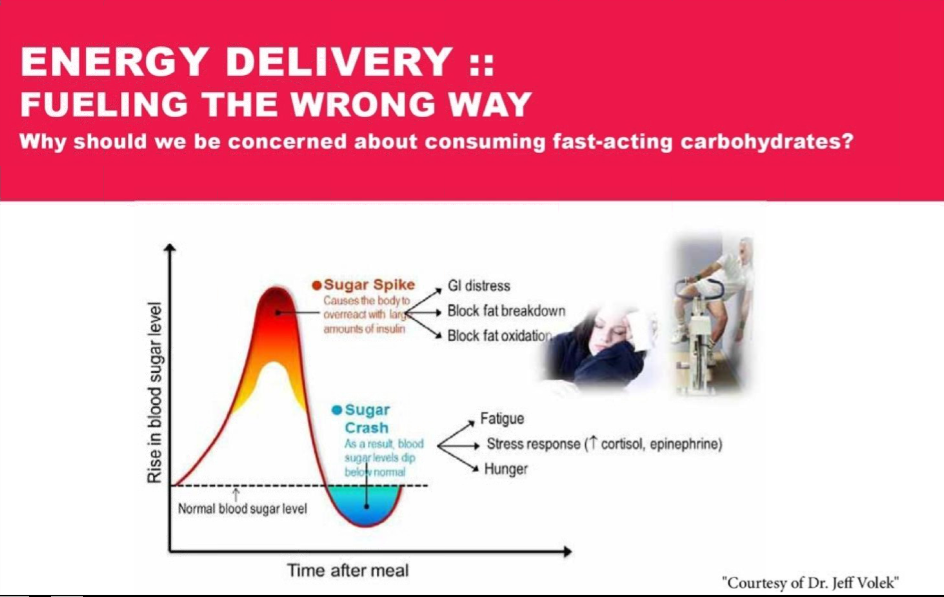
The Issue
The body shifts its primary fuel source from fat to carbohydrates as intensity levels increase. This shift is an ineffective route to optimal health and sports performance.
The typical diet induces nutritional stress. Ingest commercial sports drinks composed of simple sugars [sucrose or fructose] or maltodextrin and you get both quick energy and an unhealthy cycle of blood sugar spikes and crashes.
Insulin-stimulating carbohydrates represents an insidious path to the podium of self-destruction.
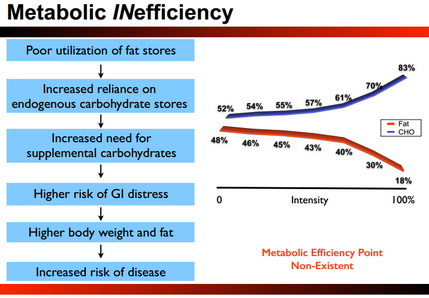
The Solution
Preservation of glycogen until it is needed ought to be the maxim. Insulin sensitivity is paramount to this process and it is attainable only via ME. Fat adaptation is paramount…
ME is the catalyst for optimal health and performance. Its profound impact on mitigating health markers while maximizing sports performance is unparalleled. It is an inside-out approach to disease prevention and sports performance.
The Benefits
–> Enhanced concentration and focus;
–> Increased sustained energy;
–> Lower caloric needs during exertion;
–> Reduced cravings;
–> Satiety;
–> Enhanced moods;
–> Better fasting blood sugar levels;
–> Improved sleep quality;
–> Accelerated body fat loss;
–> Enhanced HbA1c levels;
–> Decreased risk of chronic and degenerative diseases
The Key
ME manifests sports performance excellence because of your diet and exercise regimens — not in spite of them. A by-product of ME is its innumerable benefits respective to health markers.
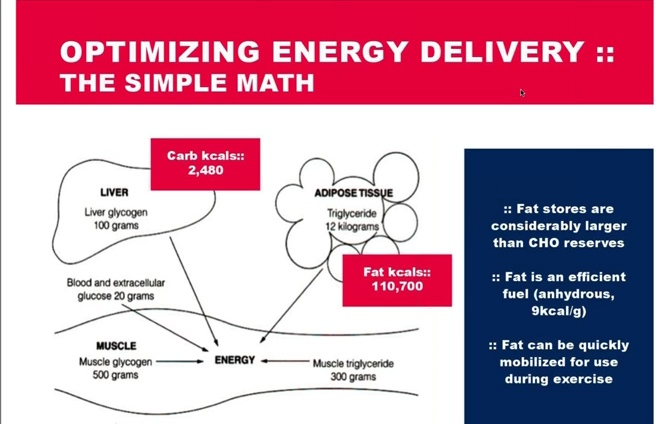
Teaching your body to oxidize fat as its primary fuel source [fat adaptation] changes the scope of longevity and performance.
Synergy is the key to your mansion of optimal health, endurance sports performance, and self-actualization. It begins and ends at the cellular level.
The Evolution
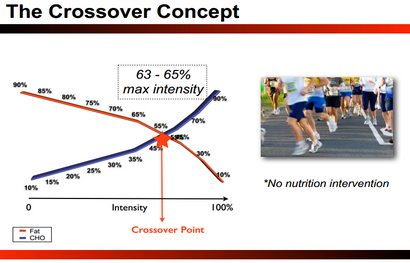
The Crossover Concept:
The Crossover Concept [CC] pinpoints the exercise intensity in which the body shifts from fat to CHO oxidation. This is expressed as a percentage of exercise intensity relative to the maximum volume of oxygen [VO2] consumed. It describes the relationship between intensity and the utilization of fat and CHO during exertion.
This concept is an exercise-only intervention. The outcome of CC is to improve fat oxidation via low-intensity aerobic training. The premise is fat oxidation will predominate when exertion is less than or equal to 63-65% of maximal intensity. The CC identifies one’s ideal “fat-burning zone” absent nutritional variables.
Metabolic Flexibility:
Metabolic flexibility [MF] is a nutrition-only intervention.
MF is the capacity to utilize fat and carbohydrate fuels plus the transition between them in response to changes in dietary energy intake or circulating substrate [enzymatic] concentrations.
MF is the ability to adapt fuel oxidation to fuel availability. The switch in fuel oxidation will depend on the type and amount of nutrients available for oxidation at the cellular level. Insulin sensitivity and insulin resistance impact MF and metabolic inflexibility, respectively.
The inability to modify fuel oxidation in response to changes in nutrient availability has been implicated in the accumulation of intramyocellular lipid and insulin resistance — precursors to metabolic syndrome.
The MF concept is based on following a low CHO daily nutrition plan before switching to a high CHO diet prior to competitions. Fat adaptation is the desired outcome.

Metabolic Efficiency:
A concept created by Seebohar complements his nutrition periodization method for peak performance and quells recurring nutrition and training issues by endurance athletes.
ME is the body’s ability to utilize endogenous stores of CHO and fat at varying exercise intensity and duration levels and rest. It is focused on the manipulation of the daily nutrition plan and the contribution of different types of exercise. It is a nutrition [75%] and exercise [25%] intervention.
ME creates the enviable quality of significantly reduced caloric intake during exertion because the body is proficient at fat oxidation even at high intensity. Its far-reaching, cost-effective benefits create a desirable approach to health and sports performance.
The ability to oxidize fat at or near one’s lactate threshold [LT] level changes everything.
Lactate threshold [LT] is defined as the exercise intensity at which lactate accumulates in the blood [lactic acid] faster than it can be extracted. It is a byproduct of the anaerobic glycolysis energy system and is commonly termed oxygen debt.
Lactic acid has received a bad rap for decades as a waste byproduct of exertion. It is now known to be easily recycled into glucose by the liver versus an inflammation-creating performance inhibitor.
Research indicates that lactate, not glucose, may be the predominant energy source metabolized by brain neurons.
Four primary reasons exist to implement the metabolic efficiency concept. These reasons impact health markers and sport performance limiters common among the mainstream and athletes.
1~Eliminates GI distress
Each person carries a limited supply of blood. Blood is necessary to transport oxygen to fuel the digestive process. This means a shortfall exists respective to the brain and musculature.
Find below typical factors that cause GI distress and gastroparesis.
–> Diversion or blood shunting;
–> Excess carbohydrate intake;
–> Osmolality imbalances;
–> Excessive water intake;
–> Exercise intensity
Becoming metabolic efficient through food combinations and exercise adaptation will balance blood sugar and manipulate endogenous fat and CHO stores to maximize performance via less caloric intake.
2~Improves nutrient partitioning for energy use
Nutrient partitioning describes whether the energy derived from the food one consumes is utilized as fuel for muscles or stored as fat. Each macronutrient and micronutrient is partitioned into either muscle or fat cells.
Insulin plays a major role in nutrient partitioning and the level of insulin sensitivity determines how the complex shuttle system functions. Insulin sensitivity has the potential to improve energy expenditure whereas insulin resistance turns your body into a fat storage facility.
Insulin stimulates the uptake and storage of glucose. Blood glucose levels surge when the small intestine breaks down CHO. Elevated glucose levels propel insulin spikes which inhibit lipolysis.
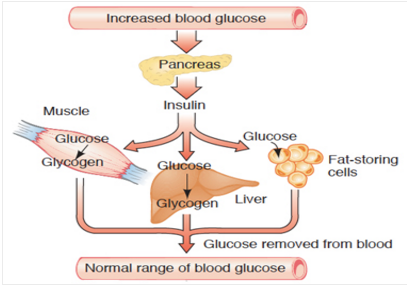
Glucose will be converted to glycogen and stored in the liver and muscles. Glucose in the bloodstream means additional insulin is released to expunge it [convert and store it as fat]. This leads to insulin resistance which first impairs muscle function before triggering other health markers.

Fat adaptation is the key:
–> Increase whole body fat oxidation, even in highly trained individuals;
–> Skeletal muscle is primarily responsible for increased fat oxidation during exercise after a short-term, high-fat diet as a result of altered substrate storage;
–> Increased fat oxidation is due to elevated intramuscular triglyceride (IMTG) concentration
3~Improves body composition and weight
Decreasing body fat is beneficial for optimal health and performance.
Body composition refers to the proportion of lean body mass (highly correlated with muscle mass) to fat mass in a person. Improving body composition involves decreasing body fat while maintaining or adding muscle.
There are a plethora of reasons for losing body fat from maintaining health and well-being, excellence in sport via improved quickness, agility, and enhanced performance, or simply to look and feel better.
Restrictive caloric dietary plans will provide insufficient fuel for exertion, compromise training adaptations, and deliver suboptimal results.
A more prudent approach is to provide adequate energy to fuel exercise and allow endogenous fat stores to play a vital role in attaining a lean athletic physique.
4~ Improves health markers and risks associated with/ chronic and degenerative diseases:
–> Mood stabilization;
–> Improved lipid profile;
–> Lower fasting blood sugar and insulin;
–> Controlled inflammation;
–> Improved memory;
–> Improved sleep quality –> Sleep deprivation is linked to high glucose concentrations which increase the risk for chronic and degenerative diseases;
–> Blood sugar Imbalances –> Impact on health and performance
Insulin not only facilitates the proper utilization of glucose but plays a significant role in other aspects of cellular function and nutrition. Insulin has been shown to affect protein metabolism, amino acid transport, neurotransmitters, nutrients, and other molecules across the cell membrane.
A system termed the sodium-potassium pump is critical to cellular homeostasis. Elevated blood sugar damages this precious system via oxidative stress, glycosylation, and hypoxia.
The system monitors cell communication, antioxidant protection, electrolyte balance, and ion regulation such as calcium, and magnesium, among others. Phosphate metabolism is the key to ion transport, mitochondrial proliferation, and muscle contraction.
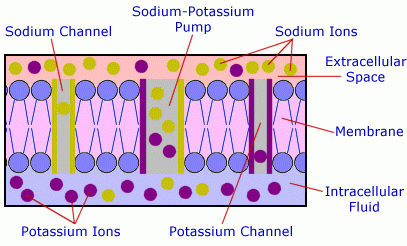
Elevated blood sugar increases insulin secretion which decreases the insulin/glucagon ratio, inhibits glycolysis, which hampers energy production. Find below some of the adverse health conditions resulting from elevated blood glucose levels:
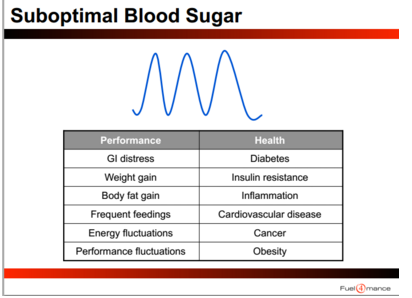
Cellular health requires synergy among four important variables: homeostasis; antioxidants, mitochondrial function; and the acid/alkaline balance. Detailing these processes is beyond the scope of this article but an overview is available in a four-part series published in Snowshoe Magazine | Cellular Foresight | http://bit.ly/1klAIev.
Testing Protocols
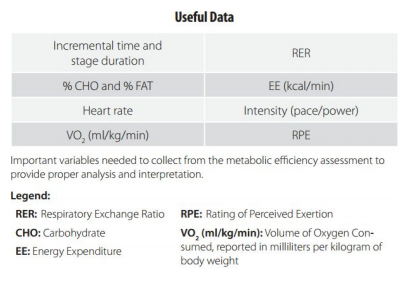
ME testing is different from all other exercise physiology testing protocols because it utilizes indirect calorimetry. Calorimetry is the science associated with determining the changes in energy of a system [www.physicsclassroom.com].
Indirect calorimetry is a technique that provides accurate estimates of energy expenditure from measures of carbon dioxide production and oxygen consumption during rest and steady-state exercise. Direct calorimetry cannot be performed on humans.
A submaximal ME test should not be confused with the coveted VO2 max test. The primary difference between the two assessments is that a submaximal test allows the body time to adapt to incremental changes. Substrate circulation [MF] must stabilize to incur a precise reading.

VO2 max is the maximal oxygen uptake utilized in one minute during maximal or exhaustive exercise. VO2 max tests can be valuable tools to train endurance athletes to attain their maximum potential. The training zones can be correlated with heart rate, perceived exertion rating, power, and pace.
Aerobic exercise significantly improves VO2 max. Though VO2 max is an excellent mode to measure fitness it is not a viable predictor of athletic performance. Enter the ME assessment.
–> ME assessments last 30-45 minutes in 5-minute increments;
–> ME assessments use lower output settings;
–> ME assessments incur precise metrics
–> VO2 max assessments last 20 minutes in 1-minute increments;
–> VO2 max assessments use higher output settings;
–> VO2 max assessments incur estimated capacity levels
Each ME assessment includes at least the following additional measurements:
–> Resting substrate;
–> Resting lactate;
–> Resting blood glucose;
–> Blood pressure;
–> Body weight;
–> Oxygen saturation
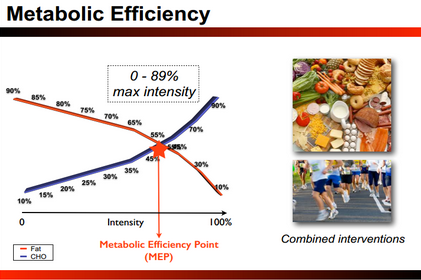
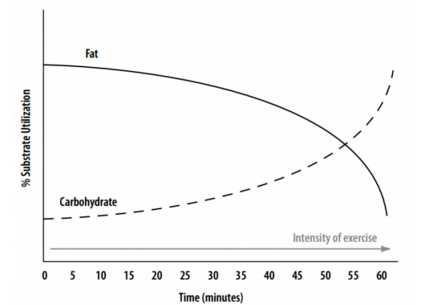
The Metabolic Efficiency Point [MEP] is the point where CHO and fat oxidation intersect during exertion. As the intensity of exercise increases carbohydrate becomes the preferred fuel source to sustain exercise.

Incremental Assessment
The goal of the incremental metabolic assessment is to determine if an individual has an MEP and, if so, what intensity it occurs.
The data will determine nutrition and exercise protocols to maximize fat oxidation at higher intensities.
Continuous Assessment
This assessment is not concerned with identifying an MEP but determining specific substrate utilization at a given intensity or varying intensities.
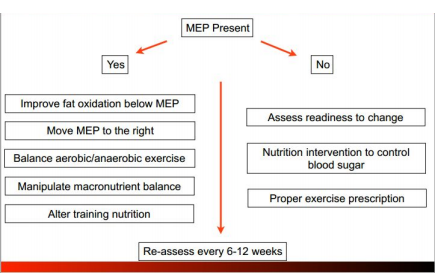
A continuous ME assessment helps an athlete create their competition day nutrition plan based on their individual fitness level at a given point in their training program. It accounts for the physiological and nutritional responses that were trained during the previous months.
It allows the athlete to dial in their nutrition more accurately based on their physiology rather than using the standard calorie and CHO ranges seen in many sports nutrition resources.
The data from a continuous assessment will ensure ME during competition thanks to prudent nutrient partitioning and exercise adaptation. Cyclists and triathletes have embraced the ME concept. These individuals are most likely dedicated to improving sports performance.
Performance Medicine™ is a medical specialty designed to genetically transcend health, performance, and longevity in life and sport.
Its principles ignite synergy – the lynchpin to optimal health and sports performance.
ME acts as the catalyst for these principles:
–> Endurance Capacity;
–> Body Composition;
–> Disease Prevention;
–> Metabolic Efficiency
Nutrition represents the cornerstone of optimal health and sports performance. Our fuel choices ought to nourish our bodies – not zap energy.
Measuring physiological and biochemical performance on a continuum where the law of diminishing returns is ever-present is a delicate balance. Implementing the requisite modifications to optimize both longevity and sports performance is paramount.
Performance Medicine™ is about synergy – mitigating health markers and maximizing endurance sports performance. The desired outcome is to educate trail, ultra, and snowshoe endurance athletes in the spirit of transcending health, performance, and longevity in life and sport.
Life begins and ends at the cellular level.
Science guides us…life leads us.
When you make the decision to honor your body – it will honor you. It is at this stage one begins to realize the difference between effort and struggle.
This changes everything…



Pingback: Genetic Propensities - Part One - SYNERGY™